- Details
- By NASA Earth Observatory
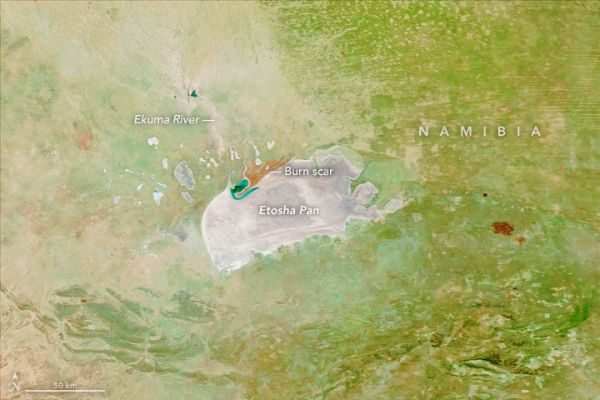
Cycles of Wet and Dry in Etosha Pan
Repeated pooling and evaporation of water built this expansive salt pan in northern Namibia.
Almost all of the 46 centimeters (18 inches) of rain that falls in Etosha National Park each year arrives between October and March. The influx of moisture—a boon for the wildlife—completely transforms the landscape. It greens parched grasslands, replenishes ephemeral streams and watering holes, and sometimes pools enough to cover a flat basin with a layer of water that extends for thousands of square kilometers.
When the rains slow and then cease during the dry season (April through September), any water in the basin slowly evaporates, depositing salt and other minerals on the land surface in the process. Over time, this cycle of flooding and evaporation has built up a mineral-encrusted surface called a salt pan. In fact, the striking white surface of the salt pan is what originally earned Etosha Pan its name. In the language of the local Ovambo people, etosha means "great white place."
Continue reading at NASA Earth Observatory
Image via NASA Earth Observatory